1. Introduction
Modern web applications are expected to be fast, responsive, and interactive. Users do not want full page refreshes for small actions like validating data, fetching values, or performing calculations. Oracle APEX supports this requirement through AJAX Callback Processes, which allow communication between the client (browser) and server (database) without submitting or reloading the page.
An AJAX Callback Process enables you to execute PL/SQL code asynchronously from JavaScript and return data back to the page. This makes it a powerful feature for building dynamic, real-time APEX applications.
2. What is an AJAX Callback Process?
An AJAX Callback Process is a server-side PL/SQL process that can be called from JavaScript using the apex.server.process API. It runs in the background and can:
- Fetch data from the database
- Perform validations
- Insert, update, or delete records
- Return values in plain text, JSON, or XML format
All this happens without page submission.
3. Tools and Technologies
- Oracle APEX
- PL/SQL
- JavaScript
- AJAX (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML)
- Dynamic Actions (optional)
4. Business Requirement
In real-world applications such as employee management, order processing, inventory systems, and dashboards, there is often a need to:
- Validate user input instantly
- Fetch related data based on selection
- Calculate values dynamically
- Save or retrieve data without interrupting the user flow
Using a full page submit for these small operations negatively impacts performance and user experience. AJAX Callback Processes solve this problem by enabling server-side logic execution in real time.
5. Creating an AJAX Callback Process
Step 1: Create the Callback Process
- Go to Page Designer
- Under Processing → AJAX Callback
- Create a new process
- Give it a name, for example:
GET_EMP_SALARY- Add the following PL/SQL code:
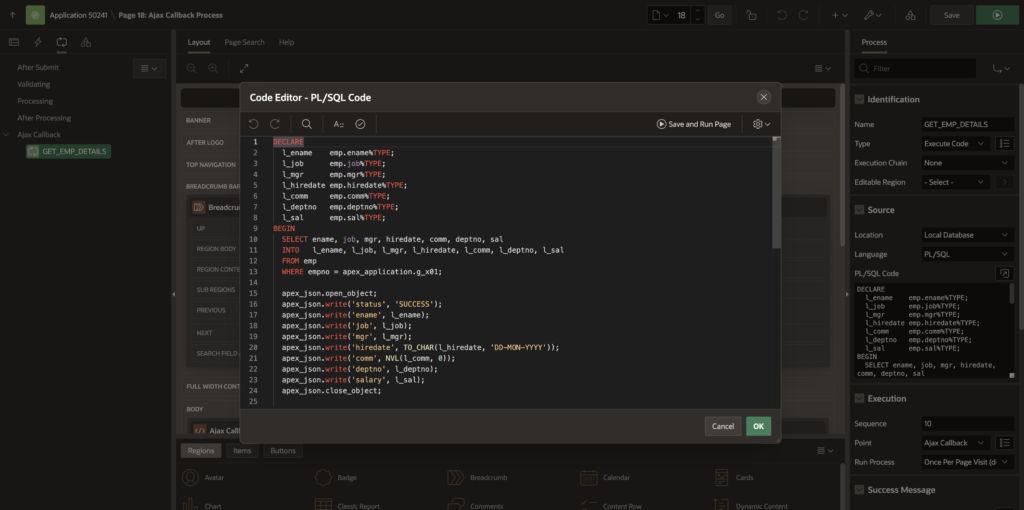
DECLARE
l_ename emp.ename%TYPE;
l_job emp.job%TYPE;
l_mgr emp.mgr%TYPE;
l_hiredate emp.hiredate%TYPE;
l_comm emp.comm%TYPE;
l_deptno emp.deptno%TYPE;
l_sal emp.sal%TYPE;
BEGIN
SELECT ename, job, mgr, hiredate, comm, deptno, sal
INTO l_ename, l_job, l_mgr, l_hiredate, l_comm, l_deptno, l_sal
FROM emp
WHERE empno = apex_application.g_x01;
apex_json.open_object;
apex_json.write('status', 'SUCCESS');
apex_json.write('ename', l_ename);
apex_json.write('job', l_job);
apex_json.write('mgr', l_mgr);
apex_json.write('hiredate', TO_CHAR(l_hiredate, 'DD-MON-YYYY'));
apex_json.write('comm', NVL(l_comm, 0));
apex_json.write('deptno', l_deptno);
apex_json.write('salary', l_sal);
apex_json.close_object;
EXCEPTION
WHEN NO_DATA_FOUND THEN
apex_json.open_object;
apex_json.write('status', 'ERROR');
apex_json.write('message', 'Employee ID not found.');
apex_json.close_object;
WHEN OTHERS THEN
apex_json.open_object;
apex_json.write('status', 'ERROR');
apex_json.write('message', SQLERRM);
apex_json.close_object;
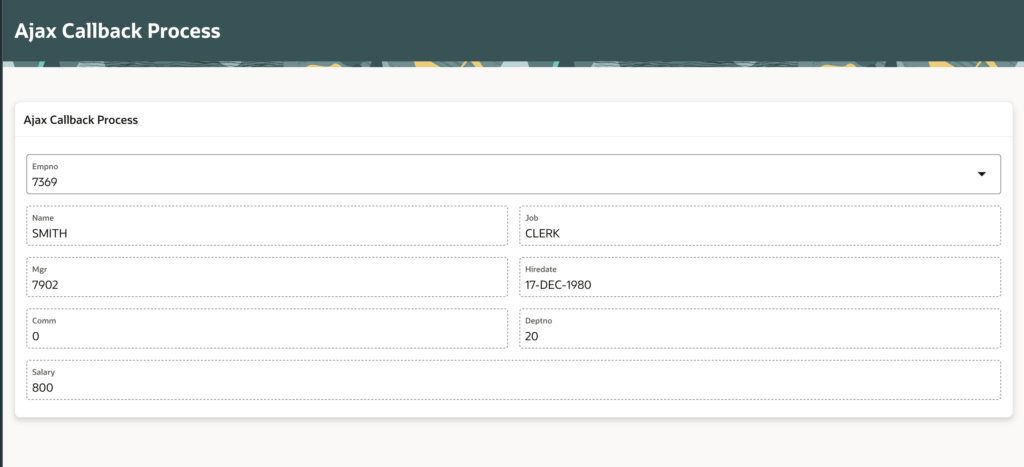
END;6. Calling AJAX Callback from JavaScript
Use apex.server.process to call the callback from the client side. Paste below code in Function and Global Variable Declaration.
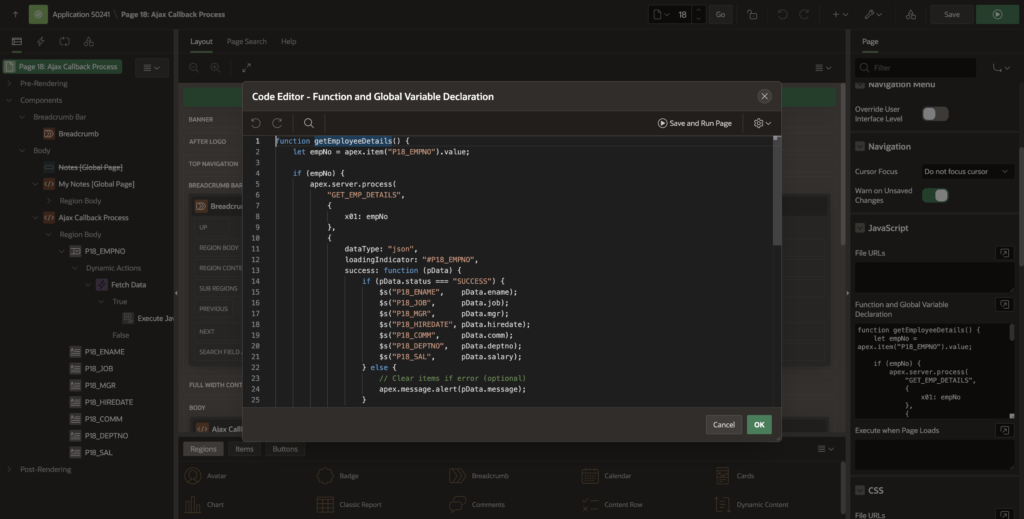
function getEmployeeDetails() {
let empNo = apex.item("P18_EMPNO").value;
if (empNo) {
apex.server.process(
"GET_EMP_DETAILS",
{
x01: empNo
},
{
dataType: "json",
loadingIndicator: "#P18_EMPNO",
success: function (pData) {
if (pData.status === "SUCCESS") {
$s("P18_ENAME", pData.ename);
$s("P18_JOB", pData.job);
$s("P18_MGR", pData.mgr);
$s("P18_HIREDATE", pData.hiredate);
$s("P18_COMM", pData.comm);
$s("P18_DEPTNO", pData.deptno);
$s("P18_SAL", pData.salary);
} else {
// Clear items if error (optional)
apex.message.alert(pData.message);
}
},
error: function (xhr, status, error) {
console.error("AJAX Error:", status, error);
console.log("Full Server Response:", xhr.responseText);
apex.message.alert("An unexpected error occurred. Please check the console.");
}
}
);
} else {
// Optional: Clear items if EMPNO is deleted
$s("P18_ENAME", "");
}
}🔹 x01 is used to pass values from the page to PL/SQL
🔹 pData contains the response returned from the server
7. Call above Javascript Function
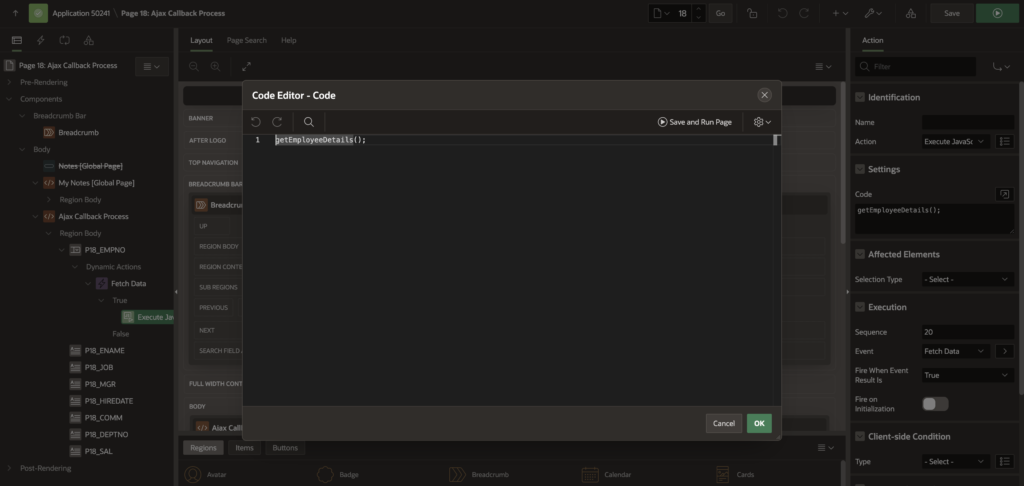
Create dynamic action on change of P18_EMPNO.
True Action=> Exicute Javascript Code
Paste below Javascript code.
getEmployeeDetails();8. Passing Multiple Values to AJAX Callback
You can pass up to x01–x10 parameters.
apex.server.process("MY_PROCESS", {
x01: $v("P1_ITEM1"),
x02: $v("P1_ITEM2")
});Access them in PL/SQL as:
apex_application.g_x01
apex_application.g_x028. Returning JSON Response
Using APEX_JSON is recommended for structured data.
apex_json.open_object;
apex_json.write('status', 'SUCCESS');
apex_json.write('message', 'Data fetched successfully');
apex_json.close_object;9. Error Handling in AJAX Callback
apex.server.process("MY_PROCESS", {}, {
success: function(pData) {
console.log(pData);
},
error: function(err) {
console.error("AJAX Error", err);
}
});You can also return error messages from PL/SQL using JSON.
10. Common Use Cases
- Dependent item population
- Real-time validations
- Calculations and summaries
- Auto-fill form fields
- Save data without submit
- Interactive Grid custom logic
11. Best Practices
- Always return JSON for complex responses
- Keep callback logic lightweight and fast
- Avoid committing inside callbacks unless required
- Add proper exception handling
- Use meaningful process names
12. Conclusion
AJAX Callback Processes are one of the most powerful features in Oracle APEX for building modern, responsive applications. By combining PL/SQL with JavaScript, you can eliminate unnecessary page submissions and deliver a smooth user experience.
Mastering AJAX callbacks will significantly improve the performance, usability, and interactivity of your APEX applications.
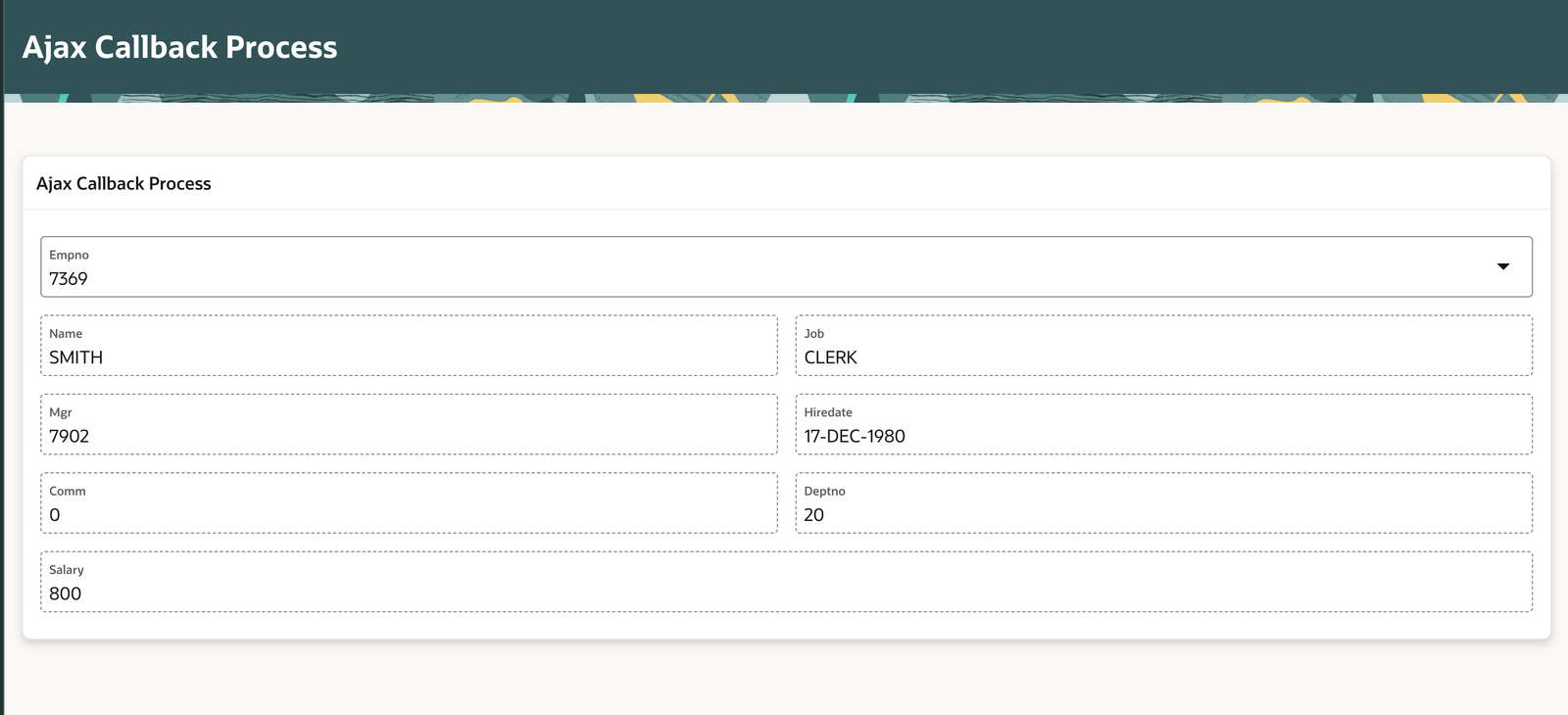
12. Output
💡 If you found this blog useful, consider sharing it with the Oracle APEX community!
Love coding? Me too! Let’s keep in touch – subscribe to my website for regular chats on Oracle APEX, PL/SQL,SQL JavaScript, and CSS.